This is our first article in the series of Data Structures and Algorithms. In this article, we will discuss the ins and outs of a Singly Linked List.
What is a Singly Linked List?
A Singly Linked List is a linear data structure that allows us to store data in a linear way. It is a collection of nodes where each node points to the next node.
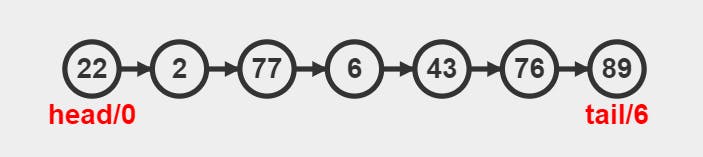
Every node contains two crucial things:
Data (integer, string, boolean, etc)
Pointer (points to the next node)
A singly linked list has two pointers of its own:
head (points to the first node)
tail (points to the last node)
The pointer of the last node always points to null since there is no node after it.
Implementation in Javascript
Now that we know what is a singly linked list and what it looks like, let's code it using JavaScript. We will be using object-oriented programming to implement it and we will use the ES6 Class syntax.
We will need two classes:
Node (represents the structure of the node)
SinglyLinkedList (represents the structure and also includes the major operations)
Node Class
As we discussed above, a node contains two things:
Data (number, string, boolean, etc)
Pointer (points to the next node)
The pointer initially points to null.
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.next = null
}
}
Singly Linked List Class
A singly linked list will have:
head pointer (points to the first node)
tail pointer (points to the last node)
length (number of nodes in the list)
class SinglyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
this.length = 0
}
}
Basic Operations
A singly linked list can perform the following operations:
push (insert at the end)
pop (remove from the end)
shift (remove from the start)
unshift (insert at the start)
get (get a node at a particular index)
set (change the value of a node at a particular index)
insert (insert at a particular index)
remove (remove from a particular index)
Now we will implement all these operations into the SinglyLinkedList class.
Push
Push will insert a new node at the end.
push(value) {
const node = new Node(value)
if (!this.length) {
this.head = node
this.tail = node
} else {
this.tail.next = node
this.tail = node
}
this.length++
return this
}
Pop
Pop will remove a node from the end.
pop() {
let currentNode = this.head
if (this.length <= 1) {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
} else {
while (!currentNode?.next?.next) {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
currentNode.next = null
this.tail = currentNode
}
this.length--
return this
}
Shift
Shift will remove a node from the start.
shift() {
if (this.length <= 1) {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
} else {
this.head = this.head.next
}
this.length--
return this
}
Unshift
Unshift will insert a new node at the start
unshift(value) {
const node = new Node(value)
if (!this.length) {
this.tail = node
} else {
node.next = this.head
}
this.head = node
this.length++
return this
}
Get
Get a node's value from a particular index.
get(index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.length) return undefined
let currentNode = this.head
for (let i = 1; i <= index; i++) {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
return currentNode.value
}
Set
Change the node's value at a particular index.
set(index, value) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.length) return
let currentNode = this.head
for (let i = 1; i <= index; i++) {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
currentNode.value = value
return this
}
Insert
Insert a new node at a particular index.
insert(index, value) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.length) return this
const node = new Node(value)
if (index === 0) return this.unshift(value)
if (index === this.length) return this.push(value)
let currentNode = this.head
for (let i = 1; i <= index - 1; i++) {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
const nextNode = currentNode.next
currentNode.next = node
node.next = nextNode
this.length++
return this
}
Remove
Remove a node at a particular index.
remove(index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.length) return
if (index === 0) return this.shift()
if (index === this.length - 1) return this.pop()
let currentNode = this.head
for (let i = 1; i <= index - 1; i++) {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
currentNode.next = currentNode.next.next
this.length--
return this
}
Time Complexity
Now that we have implemented all the basic operations that a singly linked list can perform, let's talk about the time complexity of each of them:
push: O(1)
pop: O(n)
shift: O(1)
unshift: O(1)
get: O(n)
set: O(n)
insert: O(n)
remove: O(n)
Pros and Cons of a Singly Linked List
Pros
A singly linked list is useful when you want to frequently insert or remove elements because it takes constant time.
Cons
A singly linked list is not efficient when it comes to accessing the elements because there are no indices assigned to the elements. So you have to visit each node starting from the first node until you find the target node.